![]()
Rectangular prisms
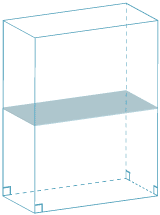
Here is an example of a right-rectangular prism. (The word 'right' is used here as a compact and convenient way of saying 'the sides are perpendicular to the base'.) Note that:
- the base is a rectangle
- if we slice it through any horizontal plane, the cross-section is a rectangle congruent to the base
- there are three right angles at each corner.
Another example of such a prism is a shoe box.
If all the sides are congruent, then we call the solid a cube.
Volume
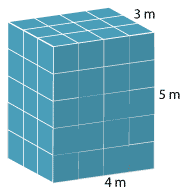
The volume of a rectangular prism is a measure of the space inside the prism.
Suppose the side lengths of the prism are 5 m, 4 m and 3 m, as in the diagram. We can cut the rectangular prism up into 1-cubic-metre cubes. Altogether there are 5 × 4 × 3 = 60 cubes. We define the volume of each cube to be 1 cubic metre, and then the volume of the rectangular prism is 60 cubic metres, or 60 m³. The side lengths of the rectangular prism are generally called the length, the width and the height, and so the volume of a rectangular prism is given by:




